A Look Back at The History of Cloud Computing
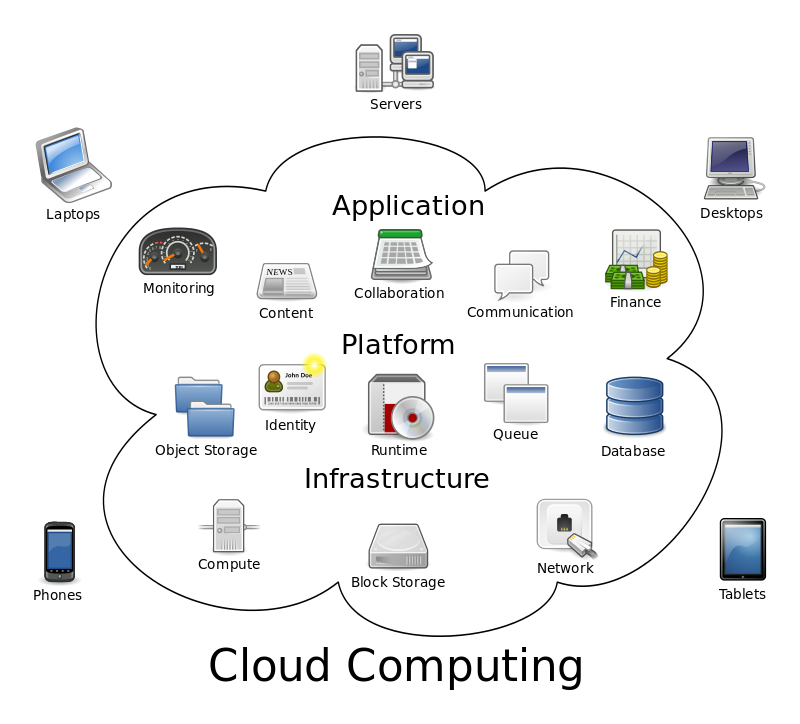
Cloud computing — the process of delivering computing as a service rather than a product — has changed the face of modern-day computing infrastructures. Both businesses and consumers alike now use the power of the cloud to improve efficiency and protect against data loss. While cloud computing has just recently picked up momentum in terms of mainstream use, the technology has been around for quite some time. This week, we’re going to take a look back at the history of cloud computing, revealing its origins and where it’s headed.
Did you know that the concept of cloud computing dates back to the 1950s? While no one knows who exactly is responsible for coining the term “cloud computing,” the concept was first seen in the 50s, when mainframe computers were used as computing hubs for client and terminal computers. The client and terminal computers did not, however, feature processors; therefore, they relied on the computing power of the mainframe units. Although rudimentary at the time, this was essentially a barebones cloud computing setup.
Fast forward to the 1960s, computer scientist John McCarthy discussed the possibility of computers be organized and used as a “public utility.” McCarthy had the bold idea of setting up a large infrastructure in which computing power could be sold as a utility, such as electricity, gas, water, etc. This idea remains on the forefront of the computing world through the 60s, 70s and 80s, but it ultimately faded into the abyss as demand for this technology died. Although McCarthy’s idea ultimately ceased to take shape, it laid the groundwork for modern-day cloud computing.
It wasn’t until the 1990s when cloud computing began to peak its head into mainstream use. Telecommunications companies during this era began to offer customers Virtual Private Network (VPN) services, which were basically private networks set up within a public network (often used for privacy reasons). VPNs are essentially a form of cloud computing since the user is routed through a network within a network.
Computer hardware manufacturers began to embrace the use of cloud computing by optimizing components for faster speeds and greater efficiency. Today, thousands of services and programs leverage the power of cloud computing. It’s an otherwise simple concept that reduces computing power waste by sending resources to connected clients. Hosted Quickbooks is one such example of cloud technology, in which third-party servers perform the computing remotely while the client simply logs in to perform his or her accounting.